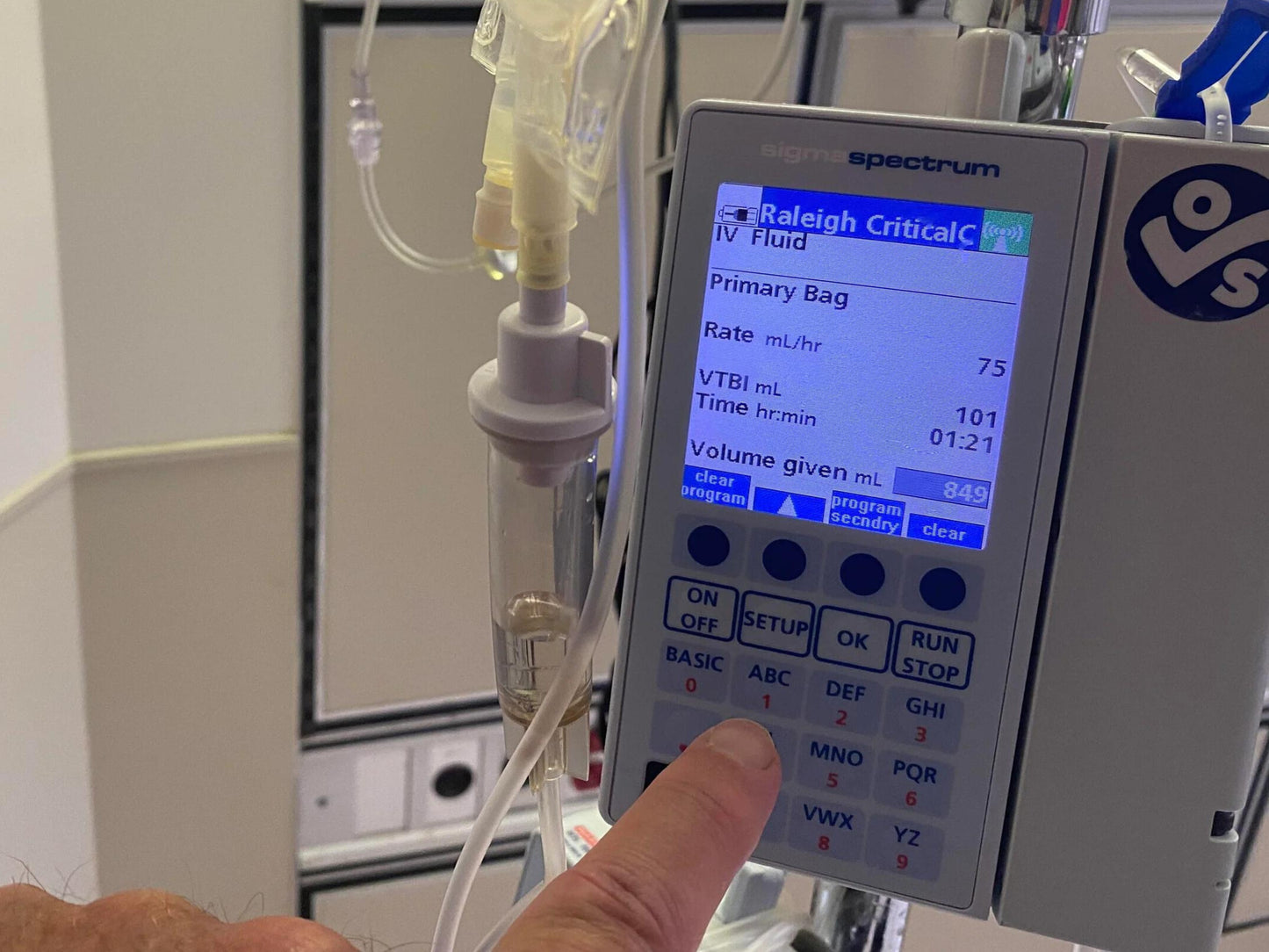
What is VTBI in Infusion Pumps?
VTBI stands for Volume To Be Infused, and it refers to the amount of fluid or medication that an infusion pump is programmed to deliver to a patient over a set period of time. The VTBI is set by a healthcare provider based on the patient's medical condition, weight, and the specific medication or fluid being administered. For example, suppose a patient requires a dose of antibiotics that should be delivered over 1 hour. In that case, the healthcare provider may program the infusion pump with a VTBI of 100 mL, meaning that the pump will provide 100 mL of...
Types of Infusion Pumps
There are several types of infusion pumps available, each designed for a specific medical application or patient need. Here are some common types of infusion pumps: Volumetric pumps: These pumps deliver a specific volume of fluid per hour and are commonly used in critical care settings such as intensive care units (ICUs) and operating rooms. Syringe pumps: These pumps use a motorized plunger to deliver medication or fluids in small, precise doses. They are commonly used in critical care settings, such as anesthesia and neonatal care. PCA (patient-controlled analgesia) pumps: These pumps allow patients to self-administer pain medication through an IV...
Syringe Pump vs Infusion Pump
Syringe pumps and infusion pumps are both types of medical devices used to administer fluids and medications to patients, but they operate differently and are used for different purposes. Here are some of the differences between syringe pumps and infusion pumps: Mechanism of operation: A syringe pump uses a motorized plunger to push medication or fluid from a syringe at a controlled rate, while an infusion pump uses pressure to deliver fluids or medication through tubing connected to a fluid reservoir. Dosing accuracy: Syringe pumps are typically used when small, precise doses of medication or fluids are required, while infusion...
Recent articles